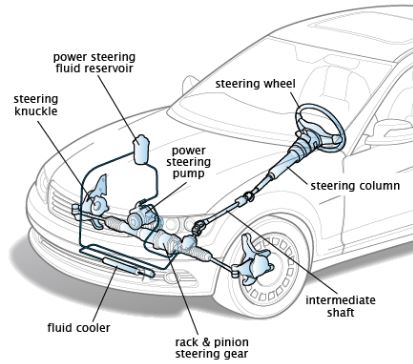
OHM’S LAW:
One of the most important electrical characteristics of a solid material is the ease
Ohm’s law with which it transmits an electric current. Ohm’s law relates the current I—or time rate of charge passage—to the applied voltage V as follows:
V = IR.
Ohm’s law expression:
where R is the resistance of the material through which the current is passing. The
units for V, I, and R are, respectively, volts (J/C), amperes (C/s), and ohms (V/A).
The value of R is influenced by specimen configuration, and for many materials is
independent of current. The resistivity ρ is independent of specimen geometry but
resistivity related to R through the expression
ρ = RA/l
where l is the distance between the two points at which the voltage is measured, andA is the cross-sectional area perpendicular to the direction of the current. The unitsfor ρ are ohm-meters(m).