What is Centrifugal Clutch?
A centrifugal clutch is a type of mechanical clutch that operates based on centrifugal force. It’s commonly used in various machinery and vehicles to engage and disengage power transmission based on the rotational speed of the engine. This extensive guide will delve into the intricacies of centrifugal clutches, covering their construction, working principles, applications, advantages, disadvantages, and more.
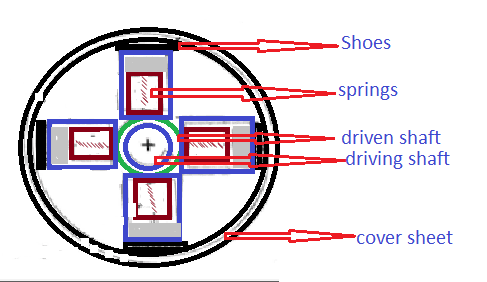
Construction of Centrifugal Clutch:
A typical centrifugal clutch consists of several key components:
- Clutch Shoes: These are semi-cylindrical shoes made of friction material. They are attached to the inner drum and are free to move axially.
- Inner Drum: The inner drum houses the clutch shoes and is connected to the engine’s crankshaft. It rotates at the same speed as the engine.
- Outer Drum: The outer drum is connected to the transmission input shaft. It remains stationary unless acted upon by the clutch shoes.
- Springs: Springs are used to hold the clutch shoes against the inner drum. They provide the necessary force to engage the clutch.
- Hub: The hub connects the clutch shoes to the inner drum, allowing them to pivot.
Working of Centrifugal Clutch:
The operation of a centrifugal clutch is based on the principle of centrifugal force. Here’s how it works:
- Idle State: In the idle state, the engine is running, and the clutch is disengaged. The clutch shoes are held against the inner drum by the springs, preventing contact with the outer drum.
- Increasing Engine Speed: As the engine speed increases, centrifugal force comes into play. It causes the clutch shoes to pivot outward, away from the inner drum, due to their semi-cylindrical shape.
- Engagement: When the engine speed reaches a certain RPM, the centrifugal force overcomes the spring tension, and the clutch shoes make contact with the inner surface of the outer drum. This engagement transfers power from the engine to the transmission input shaft, allowing the vehicle or machine to move.
- Disengagement: When the engine speed decreases, centrifugal force diminishes, and the springs push the clutch shoes back towards the inner drum. This disengages the clutch, interrupting power transmission.
Centrifugal Clutch Working Principle:
The working principle of a centrifugal clutch is rooted in the physics of rotational motion and centripetal force. As the engine’s rotational speed increases, the clutch shoes experience centrifugal force, which acts radially outward. This force pushes the shoes against the inner drum, causing them to pivot and engage with the outer drum. When the engine speed decreases, the centrifugal force weakens, allowing the springs to retract the shoes, disengaging the clutch.
For more information about cone clutches: Read Now
For more information about Plate or disc clutches: Read Now
Applications of Centrifugal Clutch:
Centrifugal clutches find applications in a wide range of machinery and vehicles, including:
- Go-Karts: Many go-karts utilize centrifugal clutches for automatic engagement, allowing drivers to focus on steering and acceleration.
- Small Utility Vehicles: Lawnmowers, garden tractors, and some small utility vehicles use centrifugal clutches for easy operation.
- Industrial Machines: Various industrial machines, such as conveyor systems and pumps, employ centrifugal clutches for power transmission.
- Motorcycles: Some motorcycles, particularly scooters and mopeds, use centrifugal clutches for automatic transmission.
- Off-Road Vehicles: ATVs and dirt bikes often feature centrifugal clutches for their rugged and versatile nature.
Advantages of Centrifugal Clutch:
Centrifugal clutches offer several advantages:
- Automatic Engagement: They engage and disengage based on engine speed, simplifying operation for users who don’t want to manually control the clutch.
- Smooth Transitions: Centrifugal clutches provide gradual engagement, reducing shock loads on the drivetrain and improving overall durability.
- Cost-Effective: They are typically more affordable than other types of clutches, making them accessible for various applications.
Disadvantages of Centrifugal Clutch:
Despite their advantages, centrifugal clutches have some limitations:
- Limited Control: Users have limited control over clutch engagement and disengagement, which may not be suitable for high-performance or precision applications.
- Heat Generation: Prolonged slipping of centrifugal clutches can generate heat, potentially leading to wear and reduced efficiency.
- Maintenance: Over time, the friction material on the clutch shoes can wear out, requiring periodic replacement.
- Limited Torque Capacity: Centrifugal clutches may not handle extremely high torque levels, limiting their use in heavy-duty applications.
In conclusion, centrifugal clutches are valuable components that simplify power transmission in various machinery and vehicles. Their automatic engagement and smooth transitions make them suitable for applications where user-friendly operation is essential. However, they may not be ideal for situations requiring precise control or high torque capacity. Understanding their construction, working principles, and applications can help users make informed decisions when incorporating centrifugal clutches into their designs or machinery.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Is centrifugal clutch used in cars?
No, centrifugal clutches are not typically used in cars. Cars primarily use friction clutches, commonly known as manual clutches, which require manual operation by the driver to engage or disengage the engine’s power from the transmission.
What is the advantage of centrifugal clutch?
The main advantage of a centrifugal clutch is its automatic engagement and disengagement based on engine speed. This feature is useful in applications like small engines, go-karts, and some types of machinery where manual clutch operation is impractical. It allows for smooth and gradual power transmission without the need for direct user control.
What is a clutch and its uses?
A clutch is a mechanical device used in vehicles and machinery to connect or disconnect the engine’s power from the transmission or drivetrain. Its primary use is to enable smooth gear changes in manual transmission vehicles by temporarily interrupting the power flow. Clutches are also used in various industrial machines and equipment to control power transfer and protect components from overload.
Is centrifugal clutch used in automatic transmission?
No, centrifugal clutches are not used in automatic transmissions. Automatic transmissions in vehicles rely on a complex hydraulic torque converter to manage power transfer between the engine and the transmission, eliminating the need for a manual clutch or a centrifugal clutch.
What is the main use of a clutch?
The main use of a clutch is to facilitate smooth engagement and disengagement of power between the engine and the transmission. In manual transmission vehicles, it allows the driver to shift gears and control the vehicle’s speed without stalling the engine or causing excessive wear on the transmission components.
Which clutch is used in automatic cars?
Automatic cars do not use traditional clutches like those found in manual transmission vehicles. Instead, they employ a torque converter, which is a fluid coupling device that smoothly transmits power from the engine to the transmission without the need for a manually operated clutch.
Is centrifugal clutch used in Scooty?
Yes, centrifugal clutches are commonly used in scooters (sometimes referred to as “Scooty” in some regions). These clutches automatically engage as the engine’s RPM increases, allowing the scooter to accelerate smoothly without the need for manual clutch control. They are a practical choice for small, lightweight vehicles like scooters.
Which clutch is used in a motorcycle?
Motorcycles typically use a manual friction clutch. These clutches are operated by the rider using a lever on the handlebars. Pulling the clutch lever disengages the engine’s power from the transmission, allowing the rider to shift gears and control the motorcycle’s speed.