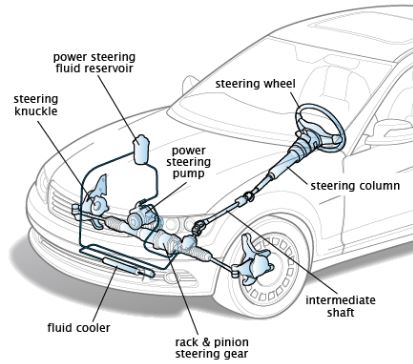
Boyle’s law:
Boyle’s law states that the volume V of a fixed mass of gas is inversely proportional to its absolute pressure p at constant temperature
i.e. p ∝ 1/V
or p = k/V
or pV = k at constant temperature, where
p = absolute pressure in pascals (Pa),
V = volume in m3, and k = a constant.
Changes that occur at constant temperature are called isothermal changes. When a fixed mass of gas at constant temperature changes from pressure p1 and vol-
ume V1 to pressure p2 and volume V1 then:
p1V1= p2V2.