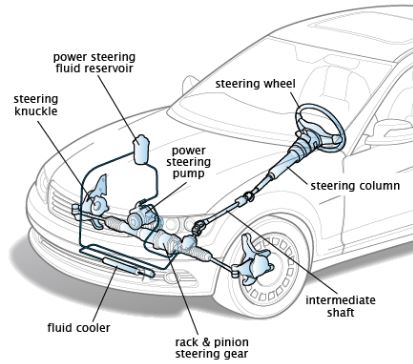
Advantages and Disadvantages of HCCI Engine?
h1 style=”text-align: left;”>What is HCCI Engine?
HCCI engines make use of the pre-ignition or hot-spark ignition that occurs in traditional diesel and gasoline engines. The process is fundamentally different from the spark ignition used by an Otto Cycle engine and much more similar to a Diesel cycle engine.
Advantages of HCCI Engine:
- Efficient use of fuel is obtained.
- Improved combustion and low emission levels.
- Low NOx emissions relative to diesel engines.
- Can be applied to a variety of vehicle types with very high torque levels from idle to top performance.
- Flexible to suit different fuels such as petrol, natural gas, or hydrogen with changes typically taking about 2 hours.
- HCCI technology has been proven over many years to have a significant advantage in fuel consumption and emissions compared with other combustions engines.
- Fuel savings over spark ignition engine because the HCCI is air-fuel ratio controlled.
- Guaranteed emission outputs due to constantly changing air-fuel ratios.
- Minimum cold startup – HCCIs can start at temperatures well below 0 degrees C (no mixture warmer than ambient temperature).
- Reliable starting, even in cold weather or after prolonged storage without use.
- There are no spark plugs or fuel injectors (though it does benefit from valves), thereby reducing internal moving parts, increasing fuel economy, and cutting maintenance costs.
- The engine is also very quiet, which could be an advantage for urban drivers.
- HCCI Engines could produce enough power, with the right detonation conditions, for an automobile.
- Power is not a consideration for HCCI engine applications, because the heat of producing the ignition produces more than enough force.
Disadvantages of HCCI Engine:
- Lack of high power output for high-demand situations given pulsing type combustion.
- Lack of precise control timing between air and fuel delivery creates a large area of overlap where the combustion occurs, which produces low temperature.
- HCCI engines are that they are traditionally less efficient than SI or CI engines.
- One drawback of Depending on the fuel used, these types of engines can have an efficiency rating anywhere from 50% up to 12%.
- The air/fuel mixture inside a gasifier needs to be hot enough for complete combustion, this type of engine doesn’t work well at high altitudes and in areas with atmospheric pressure below 18kPa.
- HCCI engine has a shorter lifespan than some other engine types.
- It also requires a higher octane fuel, which could be a problem for drivers in areas where premium fuel is not available.
- This includes potential complexities arising from unusual operating conditions where misfires are triggered by high air/fuel ratios or lean mixture flames are brought closer to pre-mature too hot mixtures may cause flame quenching resulting in misfires due to inadequate fuel injection timing.
- It’s a relatively young technology, so it’s still finding its footing. Early adopters have been disappointed because the first HCCI engines lacked low-end torque and efficiency for transportation use, which has led to the HCCI engine being relegated solely to industrial settings.