Metal Forming: Types, Applications, Advantages & Disadvantages
What is Metal Forming?
Metal Forming is a broad set of manufacturing techniques tha used to create metal parts or machined workpieces by converting raw materials into finished goods. We apply forces such as tension, compression, shear, and others to the deformed material in this process.
It is a large set of the manufacturing process by which a raw material is converted into a product. In this process, we apply stresses like tension, compression, shear, etc. to deform the raw material.
Nevertheless, there are still plenty of occasions when manufactured items can’t let go of their imperfections, which occur because it is impossible to produce everything uniformly (shape error). For example, nuts normally need slight deformations during cold rolling to prevent them from rotating inside bolts after installation – an inaccuracy which wouldn’t matter if you were using steel screws instead of bolts.”
The Forming Processes are used to make a wide variety of products, including Cars, Aircraft, Cutlery, Tools, Machinery Parts etc.
Types of Metal forming:
There are several different types of metal forming processes that can be used to shape metals into their desired form. The most common metal forming processes are as follows:
- Forging
- Rolling
- Bulk-Forming
- Extrusion
- Drawing
- Wire Drawing
- Sheet Metal Forming
- Squeezing
- Bending
- Deep Drawing
- Powder Metal Forming
- Powder Injection Molding
- Hot Forming
- Warm Forming &
- Cold Forming
In each of these processes, the metal is heated to soften the material so that it can be manipulated into its desired shape. Forming processes are also used when making parts from bulk metals.
One of the earliest types of metal forming is annealing, which is done by heating a piece of metal to just below its melting point, then slowly cooling it until it reaches its desired hardness. This process is used to soften metal so that it can be easily shaped, and it also strengthens the metal by causing the crystals to grow in size.
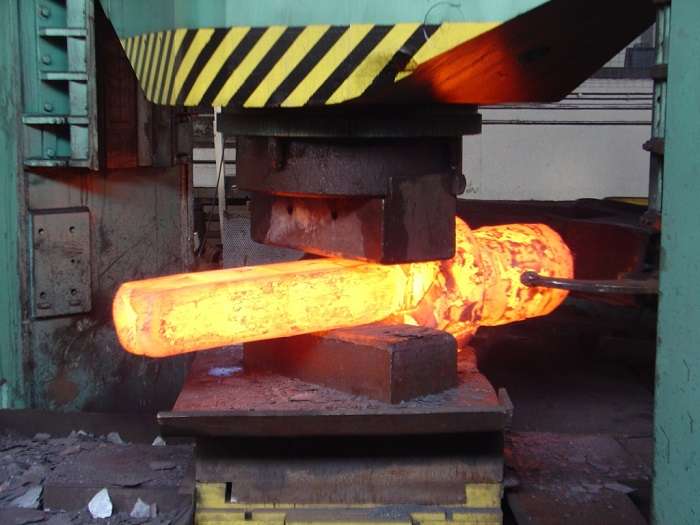
1. Forging:
- This is a process where we use a hammer to hit the metal to change its shape.
Open die forging (Image Source: Click here)
2. Rolling:
- In this process, we use a rolling machine to roll the metal into the desired shape.
3. Bulk-Forming:
- It is a process where a large sheet of metal is heated and then formed into its desired shape by using a tool or die.
- The most common type of bulk-forming is rolling, where a sheet of metal is passed between two rollers to form it into the desired shape.
4. Extrusion:
- It is a process where a small amount of metal is forced through a die to create a long, thin piece of metal. This process is often used to create rods, tubes, and wires. Forging is a process where a metal is heated until it is soft and then shaped by using a hammer or other tool. This process is often used to create parts that need to be strong and durable.
5. Drawing:
- This is a process where we use a die to draw the metal into the desired shape.
6. Wire Drawing :
- It is a process where a metal wire is pulled through a die to make it thinner. This process is often used to create wires that need to be small and lightweight. Squeezing is a process where a metal is squeezed between two dies to create the desired shape. This process is often used to create small parts that need to be strong and durable.
7. Sheet Metal Forming:
- It is a process where a sheet of metal is heated and then formed into its desired shape by using a tool or die. This process is often used to create display cases, brackets, and other similar items. Bending is a process where a metal rod or wire is heated so that it becomes soft enough to bend without breaking. This process is often used to create hooks and rods.
8. Deep Drawing:
- It is a process where a sheet of metal is placed into a die and then forced into the die using a punch. This process is often used to create metal pans, cans, and other items that are curved in shape. Shearing is a process where a sheet of metal is cut into its desired shape by using a guillotine-like machine or another type of shearing tool. This process is often used to create large sheets of metal that are then cut into smaller pieces.
9. Powder Metal Forming:
- It is a process where a small amount of metal is heated and then forced through a die to create a small, powder-like piece of metal. This process is often used to create gears, bearings, and other small parts. Powder forging is a process where a small amount of metal is heated and then forced through a die to create a small, powder-like piece of metal. This process is often used to create parts that need to be strong and durable.
10. Powder Injection Molding:
- It is a process where a small amount of metal is heated and then forced through a die to create a small, powder-like piece of metal. This process is often used to create parts that need to be strong and durable. Powder extrusion molding is a process where a small amount of metal is heated and then forced through a die to create a small, powder-like piece of metal. This process is often used to create parts that need to be strong and durable. Molding is a process where a small amount of metal is heated and then forced through a die to create a small, powder-like piece of metal. This process is often used to create parts that need to be strong and durable.
11. Hot forming:
- It is the process of shaping metal at a temperature above its recrystallization temperature. The high temperature allows the metal to deform easily, so it can be shaped into complex parts. Hot forming is used to make large parts with a high degree of accuracy.
12. Warm forming:
- It is the process of shaping metal at a temperature below its recrystallization temperature. The metal is shaped at a lower temperature, so it doesn’t deform as easily as hot-formed metal. This makes warm forming ideal for smaller parts with less complexity.
13. Cold forming:
- It is the process of shaping metal at a temperature close to its ambient temperature. The metal is shaped at a low temperature, so it doesn’t deform as easily as warm-formed metal. This makes cold forming ideal for small parts with less complexity. Cold-formed parts are also more durable than warm or hot-formed parts.
- The types of forming processes that are used will depend on the type of metal that is being used, the size and shape of the part that needs to be created, and the amount of metal that is needed.
Applications of Metal Forming:
There are a variety of different applications that can be utilized with metal forming processes. Some of the most common applications include in Following Industries
- Automotive Manufacturing
- Aerospace Engineering
- Construction &
- Press working
1. Automotive Manufacturing:
- Metal forming is extensively used in the automotive manufacturing industry. The majority of automobiles contain sheet metal that has been shaped through various metal forming processes. The metal forming process is the only way that sheet metals can be shaped into such intricate parts as automobile body panels which often consist of multiple shapes and contours.
2. Aerospace Engineering:
- Applications within aerospace engineering include airplane fuselages, wings, and engine components. While most parts used in the construction of an airplane are made from either metal or composite materials, metal is more often used in the construction of fuselages and engine components because it provides greater strength than composite material.
3. Construction:
- Applications for metal forming processes within construction include pipelines. Metal pipeline tubes are manufactured using either hydraulic or electric resistance processes depending on the desired shape. A new method called air-forming has recently become popular because it allows for the production of seamless pipes.
4. Press Working
- Metal forming is a metalworking process that changes the shape of metal using various application techniques, such as squeezing, stamping, or bending. Applications of this type are used broadly in the industry to fabricate and assemble parts and products. Two processes: hot, can be used to form metal. In hot forming, the metal is heated to a malleable state and then shaped. Cold forming is performed without heating the metal and uses force to deform it into the desired shape. The two most common applications of metal forming are press working and bending.
- Which type of forming is best for your application depends on the size and complexity of the part, as well as the desired accuracy and durability. Hot forming is best for large, complex parts, while cold forming is best for small, simple parts. Warm forming is a good option for parts that fall in between these two extremes.
Advantages of Metal Forming:
- Uses the simplest,
- Most versatile
- Lowest-cost tools.
- It can accommodate all shapes from thin sheet metal to heavy plate or tubing.
- With a little preliminary shaping, almost anything can be formed using this process.
- The products made through Forming Processes are stronger and more durable than those made through casting.
- The Forming Processes can be used to make a wide variety of products.
- The Forming Processes are more efficient than casting.
- The metal forming process is speed.
- It is a cost savings for production companies that can operate metal-forming machinery at a faster rate than conventional tooling.
- Metal forming processes gives a wide range of properties, from low-carbon steel to stainless steel and with most being available in either sheet or wrought.
- These processes allow for fabricating complex geometric shapes -But possibilities are only limited by the type of metal used and the shape required.
- Great for shaping metal because the process is quick, easy, and it produces strong shapes that can often be reused. It’s also great for repeatable tasks like production machinery.
- Higher potential strength than forging or casting because it hammers through residual stresses before they get to the surface, When using other methods like casting or forging, all stress concentrates at the surface making them more likely to crack or shatter if exposed to fatigue loads.
- Minimum use of trimming means reduced scrap costs, this benefit is amplified in mass production.
- It is a very economical process.
- It is highly versatile, as it can be used to form any number or type of shape out of metal.
- Machines are available designed for both rough and fine metal forming processes.
- Due to the process efficiency, it has already reached a degree of automation not achieved with other sorts of fabrication processes. This causes snags in production time minimalized before they happen.
Disadvantages of Metal Forming:
- High power input due to large surface area contact to ambient air which requires expensive equipment for heating and cooling. Slow cycle time–sometimes up to 1 hour per piece if one is producing long rods or lengths of pipe.
- Large variations in part thickness make it difficult to maintain accurate tolerances over the entire cross-section profile.
- Requires investment in tooling upfront.
- Metal forming will not suffice when working with solid shapes like pipes where interior volume needs to be accommodated–most likely requiring stainless steel mandrels and shearing equipment instead).
- the disadvantage of the process is susceptibility to error ratios where defects are hard to detect after processing.
- High initial cost (in both time and money) for this process because special equipment may be needed to complete it.
- Forming Processes are more expensive than casting.
- Some problems present during prolonged annealing can still be seen after reforming; this problem is partially addressed by shortening the anneal time before reforming begins.
- Heating times vary depending on materials hardness, size, thickness, or weight; if not careful
- The machine used must be fully enclosed around the material since contact between steel parts will ruin their surface finish and lengthen their lifespan.
Conclusion of Forming:
Forming Process is a large set of the manufacturing process by which raw material is converted into a product. In this process, we apply stresses like tension, compression, shear, etc. Forming Process is used to make many types of products in various industries because it has various advantages over other manufacturing processes. However, the Forming Processes also have some drawbacks which should be taken into account before choosing this process.