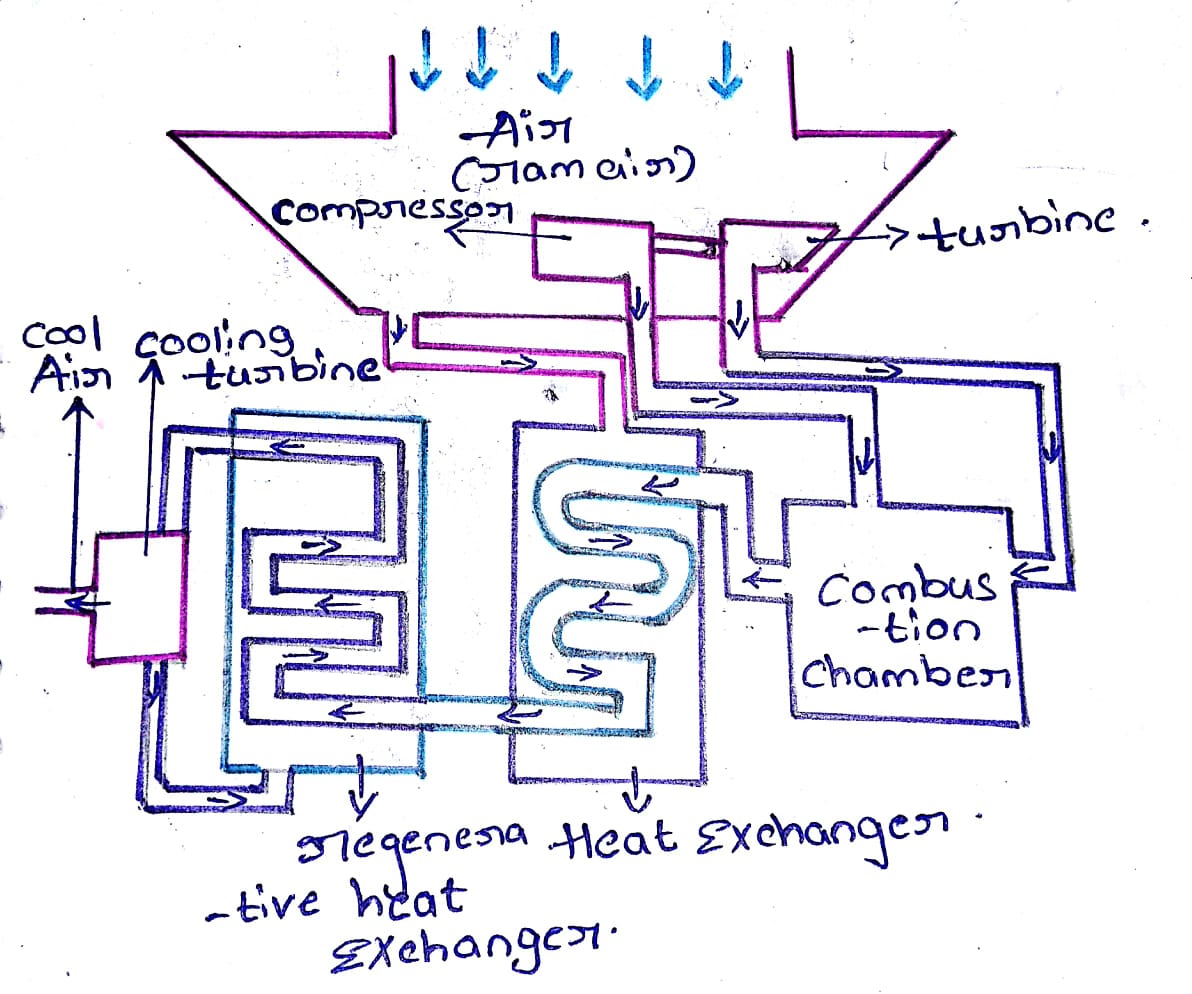
What is Simple Air Cooling System?
A simple air cooling system typically involves the basic components and processes needed to dissipate heat from a source using air as the cooling medium. Here’s a simplified explanation of the components and processes involved in a basic air cooling system:
Components of a Simple Air Cooling System:
- Heat Source:
- The heat source is the object or system that generates heat during operation. This could be electronic components, a machine, an engine, or any equipment that requires cooling.
- Heat Dissipation Surface:
- A heat dissipation surface is a component (such as a heat sink or radiator) in direct contact with the heat source. Its purpose is to provide a larger surface area for effective heat transfer.
- Air Flow Mechanism:
- The system relies on air as the cooling medium. The air can flow naturally (natural convection) or be actively circulated using fans or blowers (forced convection). Forced convection is often used to enhance cooling efficiency.
- Ventilation:
- Adequate ventilation is crucial to ensure a continuous supply of fresh air to the heat dissipation surface. This prevents the buildup of hot air around the heat source and facilitates efficient cooling.
Process of a Simple Air Cooling System:
- Heat Generation:
- The process begins with the heat source generating thermal energy during its normal operation.
- Heat Transfer to Heat Dissipation Surface:
- The generated heat is conducted to the heat dissipation surface, where it is concentrated.
- Air Flow:
- Air, drawn naturally or forced by fans, flows over the heat dissipation surface.
- Heat Transfer to Air:
- Heat is transferred from the heat dissipation surface to the surrounding air through conduction and convection.
- Temperature Reduction:
- As the air absorbs heat from the surface, it gets warmer, and the heat dissipation surface cools down, effectively reducing the temperature of the heat source.
- Air Displacement:
- The warm air rises due to natural convection or is actively displaced by fans or blowers, creating a continuous flow of cooler air over the heat dissipation surface.
- Continuous Cooling Cycle:
- The process continues cyclically as long as the heat source is active, ensuring a continuous cooling effect.
Examples of Simple Air Cooling Systems:
- Computer Cooling:
- Heat sinks and fans are commonly used in computers to dissipate heat generated by the central processing unit (CPU) and other components.
- Automobile Radiators:
- Radiators in vehicles use air as a cooling medium to dissipate heat from the engine coolant.
- Home Appliances:
- Refrigerators, air conditioners, and various household appliances often use air as the cooling medium for their internal components.
Simple air cooling systems are cost-effective and widely used in various applications. However, for more demanding or specialized cooling requirements, more complex systems, such as vapor compression refrigeration, may be employed.
Advantages of Simple Air Cooling System
Simple air cooling systems, despite their basic design, offer several advantages in various applications. Here are some key advantages:
- Cost-Effectiveness:
- Simple air cooling systems are often more cost-effective to implement and maintain compared to complex cooling systems. They generally have fewer components, reducing initial costs and potential maintenance expenses.
- Ease of Maintenance:
- With fewer components and a straightforward design, simple air cooling systems are generally easier to maintain. This can result in lower maintenance costs and reduced downtime for the equipment or system being cooled.
- No Power Consumption for Cooling Medium:
- Unlike some liquid cooling systems that require pumps to circulate coolant, simple air cooling systems rely on natural or forced convection, requiring no additional power consumption for the cooling medium.
- Simplicity of Design:
- The simplicity of the design is an advantage, especially in applications where complexity is not necessary. This simplicity can lead to quicker installation and easier troubleshooting.
- Reliability:
- Simple air cooling systems are often considered reliable due to their uncomplicated design. The absence of complex components reduces the likelihood of malfunctions and enhances overall system reliability.
- Environmental Friendliness:
- Air is a natural and environmentally friendly cooling medium. Simple air cooling systems eliminate the need for refrigerants or other chemicals, reducing the environmental impact associated with some cooling methods.
- Suitability for Small-Scale Applications:
- Simple air cooling systems are well-suited for small-scale applications, such as cooling electronics, appliances, or small machinery. They provide effective cooling without the need for elaborate infrastructure.
- No Risk of Fluid Leakage:
- Unlike liquid cooling systems, which carry the risk of fluid leakage, simple air cooling systems do not involve the use of liquids. This eliminates the potential for spills and damage to equipment.
- Versatility:
- Simple air cooling systems are versatile and can be applied to a wide range of applications, including electronics, engines, and industrial processes. Their adaptability makes them suitable for diverse cooling needs.
- Energy Efficiency in Some Cases:
- In certain situations, simple air cooling systems can be energy-efficient, especially when natural convection is utilized. Passive cooling methods can contribute to energy savings in environments where fans or blowers are not required.
While simple air cooling systems offer these advantages, it’s essential to note that they may have limitations in terms of cooling capacity and precision compared to more sophisticated cooling methods. The suitability of a simple air cooling system depends on the specific requirements and constraints of the application.
Disadvantages of Simple Air Cooling System
While simple air cooling systems have several advantages, they also come with certain disadvantages, particularly in situations where more advanced cooling methods might be required. Here are some drawbacks associated with simple air cooling systems:
- Limited Cooling Capacity:
- Simple air cooling systems may have limited cooling capacity compared to more advanced methods like liquid cooling or vapor compression refrigeration. This can be a significant drawback in applications with high heat loads.
- Temperature Control Challenges:
- Achieving precise temperature control can be challenging with simple air cooling systems. The cooling effect is influenced by ambient conditions, and maintaining a specific temperature range may be difficult.
- Ineffectiveness in High-Temperature Environments:
- In environments with already high temperatures, simple air cooling systems may struggle to provide effective cooling, as the temperature difference between the cooling medium (air) and the heat source diminishes.
- Dependence on Ambient Conditions:
- The performance of simple air cooling systems is highly dependent on ambient conditions, such as air temperature and humidity. Variations in these conditions can impact the efficiency of the cooling process.
- Noise Generation:
- Systems that use forced convection, such as fans or blowers, can generate noise. In some applications, especially those requiring a quiet environment, the noise produced by these components may be a disadvantage.
- Limited Applicability in Large-Scale Systems:
- For large-scale applications with substantial cooling requirements, simple air cooling systems may not be sufficient. More complex and efficient cooling methods might be necessary to meet the demands of such systems.
- Risk of Overheating:
- In scenarios where the heat load exceeds the cooling capacity of the air cooling system, there is a risk of the equipment or system overheating. This limitation can be critical in applications where precise temperature control is essential.
- Potential for Hotspots:
- Simple air cooling systems might not distribute cooling evenly, leading to hotspots in certain areas. This uneven cooling can affect the performance and lifespan of electronic components.
- Limited Flexibility in Temperature Control:
- Achieving specific temperature setpoints may be challenging, especially in situations where natural convection is the primary cooling method. Fine-tuning the temperature control might require additional components or strategies.
- Less Effective in Confined Spaces:
- In confined spaces with limited airflow, simple air cooling systems may struggle to dissipate heat effectively. This limitation can be significant in applications with spatial constraints.
It’s important to carefully consider the specific requirements of an application when choosing a cooling method. While simple air cooling systems are suitable for many applications, more sophisticated cooling methods may be necessary in situations where their limitations could impact performance and reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQ’s
Can simple air cooling systems be used in noise-sensitive environments?
Forced convection systems with fans or blowers can generate noise. In noise-sensitive environments, it’s essential to consider the noise level and explore quieter cooling alternatives.
Are there any environmental benefits to using a simple air cooling system?
Yes, simple air cooling systems are environmentally friendly as they typically do not involve the use of refrigerants or other chemicals that may have environmental impacts.
What types of applications are suitable for simple air cooling systems?
Applications include cooling electronics (e.g., computer components), appliances, and smaller machinery where simplicity and cost-effectiveness are prioritized.
Can simple air cooling systems achieve precise temperature control?
Achieving precise temperature control can be challenging due to dependence on ambient conditions. More advanced cooling methods may offer better temperature regulation.
Do simple air cooling systems require additional power for cooling?
Natural convection systems do not require additional power. Forced convection systems, using fans, require minimal power compared to some liquid cooling methods.
Are simple air cooling systems suitable for large-scale applications?
They may have limitations in cooling capacity, making them less suitable for large-scale applications with high heat loads. More advanced cooling methods might be required.
What are the advantages of a simple air cooling system?
Advantages include cost-effectiveness, ease of maintenance, no power consumption for the cooling medium, simplicity of design, reliability, and environmental friendliness.
What are the main components of a simple air cooling system?
Components include a heat source (e.g., electronic components), a heat dissipation surface (e.g., heat sink), and a method for air circulation (natural or forced convection).
How does a simple air cooling system work?
The system transfers heat from a heat source to a heat dissipation surface, and air, either through natural convection or forced by fans, circulates over the surface, carrying away the heat and cooling the source.
What is a simple air cooling system?
A simple air cooling system is a method of dissipating heat from a source using air as the cooling medium. It typically involves natural or forced convection to transfer heat to the surrounding air.